
George Browning, Eureka Stockade, 1854, 1985-9. The City of Ballarat Historical Collection, reproduced with permission from The City of Ballarat. Is this a primary or secondary source of historical information? Do you think it is an accurate representation of the Eureka Stockade Battle? Why/why not?
There are many parts of the Eureka Rebellion (also known as the Eureka Stockade) story that we know are historical facts, but there are many other parts that will forever remain uncertain, and even unknowable. This should not stop us from being curious about this interesting and important event in Australian history, as history is full of uncertainties. Sometimes these can be solved by more research, or even new ways of collecting and examining evidence, but sometimes they have to remain a mystery. The history you learn in the school subject often called History or Humanities is driven by the curiosity of academic historians, and their job is tell the truest version of our history. This can change over time when new evidence is found, or when evidence is interpreted from a new perspective.
Ultimately, stretching our critical and creative thinking muscles is really important in the study of history.

So, what can we know about the Eureka Rebellion?
Historians know for a fact that this famous Australian event occurred on Sunday, 3 December 1854. How is this knowable? Historians can find lots of primary source evidence that was written by people who experienced the Eureka Stockade Battle and all claim the event happened on this day. Here are two examples (1, 2) of such primary sources that corroborate (which means agree with each other) to tell us that the date this event happened was indeed Sunday, 3 December 1854.
Here is another: In his famous book about his experience of the Eureka Stockade Battle, Raffaello Carboni wrote in Chapter 1:
‘Brave comrades in arms who fell on that disgraced Sabbath morning, December 3rd’.

Charles Doudiet, Eureka Slaughter 3rd December, 1854. Ballarat Fine Art Gallery Collection. Reproduced with permission from Wikipedia Commons. Is this a primary or secondary source of historical information? Do you think it is an accurate representation of the Eureka Stockade Battle? Why/why not?
When historians can agree on something like a date, we can be very confident that such a detail is an historical fact. In the same way, we can know for a fact that it was a fight between Redcoat soldiers and a group of (mostly European) goldminers, and that people on both sides died on the day of the battle.
What is currently unknowable about the Eureka Rebellion?

Aunty Marlene Gilson, Surviving on the Goldfields, 2014. Reproduced with permission from the Gold Museum – The Sovereign Hill Museums Association. Aunty Marlene paints Wadawurrung oral histories to document her ancestors’ experiences of 19th century life. Is this a primary or secondary source of historical information? Do you think it is an accurate representation of the Eureka Stockade Battle? Why/why not?
There are some parts of the story that historians do not agree on, and they probably never will. These are uncertainties, or things we cannot currently know based on the available historical evidence. For example, there is a debate about exactly where the Eureka Stockade Battle took place, and just how many people died as a result of it. There are questions around the role of women and children in the days leading up to, and during, the fight itself. A Wadawurrung oral history that has been passed down from generation to generation also exists. It describes Europeans running to the Aboriginal camp near the stockade to keep safe during the fighting – you can learn more about this here. While there is some evidence to support all of these aspects of the Eureka Rebellion story, we cannot be completely confident that these stories are true, and we may never be able to know for sure. And that is okay – we should still learn about them as possible truths about this historical event.
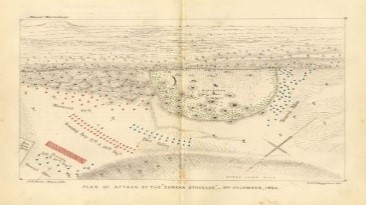
Samuel Huyghue, Plan of the Eureka Stockade attack by the military on 03 December 1854, 1854. Reproduced with permission from Ballarat Heritage Services Picture Collection. Is this a primary or secondary source of historical information? Do you think it is an accurate representation of the Eureka Stockade Battle? Why/why not?
All historical stories contain facts and uncertainties; we simply have to keep our versions of the story honest by stating which parts we can know, and which parts are currently unknowable. For example, in our popular Education Session for visiting students called Put Yourself in the Eureka Story (during which the whole class dresses up as characters who played a role in the Eureka Stockade Battle), we say ‘about 30 people died’ when talking about the battle death toll (the number of people killed) because we will never know for sure. Some reasons why we will never know exactly how many people died during the Eureka Stockade Battle are:
- There is no police report from after the battle stating exactly how many dead bodies were found on the battlefield that day, and newspaper reports and books written by witnesses claim different death tolls. Also, due to the complicated politics linked to this event, the government of the time may have wanted to make the death toll look small, while the miners may have wanted the death toll to look large – this may explain why different primary source documents describe different numbers in their death tolls. You can view the list of people whom Peter Lalor believed were killed in the Eureka Stockade Battle here. However, Captain Thomas, leader of the Redcoat soldiers who fought in Ballarat, reported a different death toll:
‘The number of the killed and wounded on the side of the insurgents was great, but I have no means of ascertaining it correctly; I have reason however to believe that there were not less than thirty killed on the spot, and I know that many have since died of their wounds. Amongst these, and the persons in custody, several leaders of the insurrection appear, two of whom lie dangerously, if not mortally wounded, in hotels near the spot.’
- Many of the miners who survived the battle went into hiding immediately afterwards to avoid being arrested by the police. During their many months in hiding, some may have died from their battle injuries. However, as they were on the run from the law, it is likely their deaths were never reported to the authorities.
- Medicine in the 19th century was not as advanced or informed as it is now – you could die from an infected scratch (because we didn’t know about germs, let alone antiseptics or antibiotics, in the 1850s). As a result, there may have been people who died from their battle injuries a whole year after 3 December 1854, and these deaths were probably not added to the official count of people killed as a result of the Eureka Stockade Battle.

The original Eureka Flag, on display at the Eureka Centre in Ballarat. Reproduced with permission from the City of Ballarat Historical Collection. Photo credit: Tony Evans Photography.
There are also historical uncertainties surrounding the most famous Eureka Rebellion artefact – the Eureka Flag. While recent scientific study of the flag has helped us better understand what the flag is made of, we will never know exactly who made it. For example, there is a popular children’s book called ‘The Night We Made The Flag: A Eureka Story’ by Carole Wilkinson, in which the stars of this famous flag are described as being made from a girl’s nightdress. However, since this book was published, museum conservators have undertaken some study of the flag stars to reveal they are made from a wool fabric, which 19th century fashion experts tell us was not the kind of material used to make nightdresses. Before this research was undertaken, the stars were believed to be made of a fine cotton linen, from which nightdresses were commonly made at this time in history. The blue part of the flag used to be thought of as wool, but this new research tells us it is mostly cotton. This demonstrates how important it is to keep our minds open as to how the flag was made; the nightdress explanation was just a theory which has now evolved and been made less certain thanks to this new research.
Until new evidence or new ways of undertaking research come to light, many aspects of the Eureka Rebellion story have to remain unknowable. What other historical events or characters have question marks hanging over them?
Links and References
Some older Sovereign Hill Education blogposts on the causes of the Eureka Rebellion:
https://sovereignhilledblog.com/2015/10/22/why-do-i-have-to-learn-about-the-goldrush/
https://sovereignhilledblog.com/2012/02/17/what-caused-the-eureka-stockade/
https://sovereignhilledblog.com/2012/06/19/what-caused-the-eureka-stockade-part-2/
https://sovereignhilledblog.com/2013/02/27/what-caused-the-eureka-stockade-part-3/
Behind The News (BTN) on the Ballarat gold rush and Eureka Rebellion: http://www.abc.net.au/btn/story/s3900125.htm
A video entitled ‘Eureka Stockade: Riot or Revolution’: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kry-xiVYMJc
The State Library of Victoria blogpost on the Eureka Stockade: http://ergo.slv.vic.gov.au/explore-history/golden-victoria/impact-society/eureka-stockade
The State Library of New South Wales on the Eureka Stockade: http://www.sl.nsw.gov.au/stories/eureka-rush-gold/rush-victoria
The National Museum of Australia on the Eureka Stockade: http://www.nma.gov.au/online_features/defining_moments/featured/eureka_stockade
No matter how the Eureka Stockade is represented, there will always be people who critique its interpretation: https://www.theage.com.au/national/the-eureka-myth-20041023-gdyus1.html
How to encourage critical thinking in History: https://sheg.stanford.edu/history-lessons
Five ways to improve your critical thinking: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dItUGF8GdTw









Australia has so much history to offer. I have given a tweet out to this post by the way to share this post. If only more schools encouraged participation in these programs. I know in NSW we have a place called timbertown, my school used to take me out there for the day. But now I am engaged in the University Life, I do not have the time to go back out to Timbertown and experience these kinds of programs. I remember when I was a child, I had so much fun and learned so much. I even got to feed the chickens! Thanks for sharing!
Omg so helpful for my essay